- Project Management Basics Ppt
- Construction Project Management Basics Pdf
- Construction Project Management Tutorial Pdf
- Software Project Management Tutorial Pdf
- Agile Project Management Tutorial Pdf
In this post we are sharing the Basics of Project Management – IES Master PDF and Paid search link for free.. This book is very useful for your for competitive exams.
Basics you need to succeed in your role, including: what a project is, the skills you need to make things run smoothly, and the 5 phases of a project—including getting things kicked o! Right and wrapping. The content of this book are highly useful for ESE – 2021 Prelims: Paper- 1: Basics of project Management. It covers the entire Engineering Aptitude and Reasoning topics that a student appearing.
About the Book
Interest in project management remains fairly high, though there has been some decline in recent years. However, the practice of project management remains questionable, as project failures continue to be. Basic Project Management: Five Steps The following steps comprise the project management roadmap. The steps may overlap and be iterative: 1. Define and Confirm Scope/Requirements 3.
Basics of Project Management – IES Master
| ISBN-10 | 9388080777 |
| ISBN-13 | 978-9388080774 |
| Publisher | IES Master |
| Author | IES Master |
| Book Type | Textbook |
| About Publisher | IES Master |
| Publishing Year | 2021 |
| Shelf Category | Higher Education |
| Pages | 208 |
| Binding | Paperback |
| Language | English |
| Edition | 2021 |
| Exam | Competitive Exams |
| AVAILABLE ON AMAZON | |
| PDF Link Tool (100+ Websites) | Kindly Wait We Are Searching The Latest Edition Of This Book... |
| Telegram Group |
Disclaimer: We DO NOT SUPPORT PIRACY - PDF Link Tool is designed by CoachingNotes.In which don't show PDF links without Publication/Author permission. If PDF is not found then PDF Link Tool will automatically show affiliate links to the user. If you have any query kindly email us on - noteshelpline@gmail.com with subject line - 'Copyright Issue'
[PDF] Basics of Project Management - IES Master - CoachingNotes.In
Basics of Project Management - IES Master
URL: https://coachingnotes.in/pdf-basics-of-project-management-ies-master/
Author: IES Master
4.3
The article provides an introduction to Project Management basics.
It can be useful for both – newbies in PM areas in order to learn something new and for experienced PMs for refreshing their knowledge.
The page contains:
- Main project fundamentals
- Keywords and basic terms (glossary)
- PM lifecycle and phases (a step by step approach)
- Infographic in PDF for free download
So let’s start.
What is a project?

Each project is something temporary and provides unique product/s or service/s.
What does it mean temporary? It means that this is not an everlasting ongoing activity but it has a START point and END point.
So, if you need to manage a project pay attention when and how it starts and when/how it ends. If you do not have answers to these questions, you will be in trouble soon.
What is “unique” product/s or service/s? It is simple – you are doing something NEW and this will lead you somewhere no one has been before.
It can be scary, especially for your team members, so you need stay calm, have the courage and to embrace the CHANGE.
Because each project changes something for someone.
What is Project Management?
Project Management includes the activities needed for fulfilling successful project. It combines the processes, knowledge, skills, and methods to achieve the project goals.
Let me get my short and simple answer first. You have AS-IS situation. You need to move to other partially defined TO-BE situation.
What do you need to do?
First, you need to define TO-BE. It is your goal. It might be satisfying customer need, or a product improvement, or legal requirements. Anyway, you need to know it, to communicate it, to repeat in day after day. By the way, business analysis techniques come quite handy when you defining your goal.
Project Management Basics Ppt
Second, you need to define AS-IS. People forget about it. But this is important. For example, if you have software project is quite handy to know the level of your developers per area. Or the maturity of your company’s products.Or your business environment and competitions. In short – you need a domain knowledge and it requires some time to be built.
Third, obviously, the steps required from AS-IS to TO-BE. Those activities are the basic of project management. All that balancing of scope, time, cost, budget, resources, risks is here.
What is the role of a Project Manager?
Project Manager is the person responsible for achieving the project goals.
For that reason, the organization provides him/her with human resources, authority to change whatever is within the project boundaries, budget, defined goal, acceptance criteria, etc.
In order to be successful one Project Manager needs knowledge in PM best practices, leadership, domain knowledge and soft skills.
In short a PM has authority provided by the company and responsibility for achieving project goals.
Project Manager vs Operational Manager
This is a very important difference when it comes to project management basics and introduction. Operational Managers are usually responsible for ongoing activities as manufacturing, accounting, logistics, etc.
Their actions are not defined as “temporal” or “unique”.
Nevertheless, many of the project requirements and projectdeliveries are related to Operational Managers day-to-day activities.
So smart PMs usually pay attention to Operational Managers goals and needs.
Stakeholders
A stakeholder is any person who is impacted by the project and can impact on the project (both in a positive or negative way).
This means that the stakeholder is not only the customers but his/her employees who will use the software. Not only the business developer who wants the project to end successfully but the Security Manager who can stop the project if he/she finds risks (negative impact).
Project Lifecycle and Phases
This is a crucial part of the basics of project management. Each project has a life cycle which is separated on phases.
- Initiation
This is a pre-project phase. Usually, managers, business developers, marketing experts discuss and decide which project to start.
Project Manager is not deeply involved here but he/she can support those initiation processes with domain knowledge, known risks, AS-IS situation expertise, etc.
This Initiation phase ends with Project Charter which is the first step of a project. Also, a list of the major stakeholders is created.
Construction Project Management Basics Pdf
- Planning
The most important and the most time-consuming phase for the Project Management. There are plenty of tasks here and the most important are:
- Define Project Plan
- Scope Management (Requirements, Scope Statement, Work Break Down Structure)
- Time Management (Tasks estimations and sequence)
- Cost Estimation
- Plan Quality, Risk Management, Communication, Human Recourses plans.
Frankly speaking, in an environment full of pressure, it is quite difficult to prepare everything on time before the project start. But there are 2 things mandatory for the good project managers:
First,you will definitely need Scope Statement and Work Break Down structure. This is TO-BE situation.
Second, you will need at least basic Project Plan with information who is who, who is responsible for what, how the change will be managed, what are the main processes, what are the main acceptance criteria. These are basic project management steps. They define how to reach TO-BE state.
- Execution
Construction Project Management Tutorial Pdf
PM tasks are less here than in planning but they are even more difficult. The 2 main tasks:
- Manage the team – this is where your team starts to do the work. So, you need to manage it. And here you will need not only the authority of your position but all of the soft-skills in order to motivate the team.
- Manage stakeholders expectations – 2 reasons for that:
- We ain’t living in a perfect world. There is no 100% correct planning. If your team stuck in somewhere you need to communicate the issue with the stakeholders. Just remember – bad news early is half bad.
- In 99% of your projects, stakeholders will require changes. Many reasons for that – new business demands, markets needs, forgotten features. Nevertheless, it is PM task to manage those changes from stakeholders to the team and back.
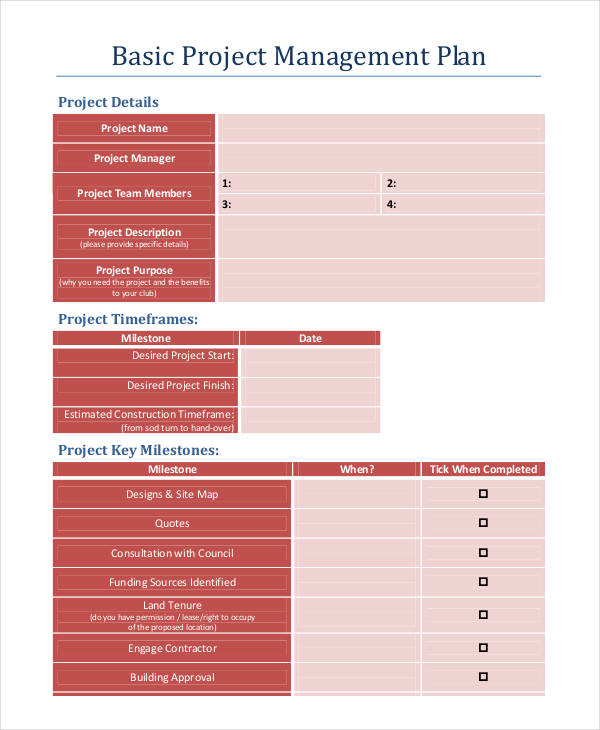
Software Project Management Tutorial Pdf
Execution phase ends with the delivery to the stakeholders. In a software project, this is mostly UAT (user acceptance test) sign-off.
- Monitoring / Controlling
Agile Project Management Tutorial Pdf
Ongoing activities due to all of the project phases. In any moment a PM needs to know where is now, where should be the plan and what is the deviation.
- Closing
The most important things here are:
- Lesson-learned session – a nice way to improve your future performance. You can discuss what went bad, what went well, and what can be improved in the future.
- Archiving the project documents – very useful for future projects. Both business and technical experts can benefit from the collected knowledge.
Basic Project Management Terms (Glossary)

To make project management basics more clear to you, here is a list of the most important PM terms and glossary with a short explanation.
- Project Charter– the document which gives authority to the Project Manager and contains high-level requirements and the most important stakeholders. The end of initiation phase.
- Kick-off meeting – the first official meeting between Project Manager and the team. It is project manager’s responsibility to organize the meeting. The goal of the Kick-off is PM to announce project goals, high-level requirements, project processes, to introduce the team member, etc.
- Requirement – a business need of stakeholders, defined of the Business Analyst.
- Business Analyst – a person responsible for revealing business needs from various stakeholders, managing these business needs, explaining them to the team, preparing a set of documents based on them, etc. The business analysis process is vital for the project success.
- SWOT analysis – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Treads. Business analysis tool for taking decisions.
- Vision Document – a high-level analysis document.
- BRD – Business Requirement Document – a detailed document with all requirements, use cases, business rules, assumptions related to a project.
- WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) – hierarchical decomposition of the work in one project. The purpose of WBS is to decompose Scope Statement to smaller and more manageable packages. For me, it is a good practice to decompose the work until I have packages which can be assigned to one team member.
- Scope Creep – uncontrolled change of project scope. This is one of the biggest issues and it is a PM job to control it.
- Task – an action which should be done in order to achieve something. The tasks should have the owner, start date, end date, duration, predecessors, and dependencies.
- Task Overlap – a technique in which a task starts before its predecessor is finished. Increase the risk but reduce the time (in best case scenario).
- Milestone – an important moment in the project. Usually, some set of tasks should be done till/on this moment. Milestone is a task with no duration.
- Critical path – a technique used to complete a project on time. It focuses on key tasks. It is PM responsibility to define Critical path tasks and to pay close attention to them. For example – best resources should be allocated on the Critical Path. To stay on track, the Critical Path is a must-have.
- Lags –defines the time between the end of one task and start of the next task/s. Example – If you paint walls into an apartment you might need one day after painting, before starting with furnishing.
- Lead – defines the time before finishing a task when the next task can start. For example testing (creating test cases) can start 2 days before the end of development.
- Estimations – an assumption for a time needed for finishing a task. Many various techniques can be used.
- Gantt chart – a popular method for visualization of tasks, task duration, relationships, owners, start and end dates.
- Business process – a chain of related tasks which defines the steps to achieve some goals – products, service, etc.
- CR (Change Request) – a change requested after some signed agreement. For example change of scope in the execution phase. It is always formal, and it is PM job to analyze its impact on scope, cost, time, risks.
- Scope, Cost, Time triangle – the most important indicators of the projects are in close relations. For example, if we increase the scope, this will impact on Time and Cost.
- Resource, Risk, Quality triangle – this is the “minor” triangle but still its managing is PM responsibility.
- RACI Matrix – responsibility matrix which defines “who is who” in a project with his/her contacts and responsibilities. Simple, but extremely useful tool. It can save a great amount of time and the team can avoid wrong processes.
- SPI – Schedule Performance Index – this index measures progress achieved vs planned progress. A value above 1.0 indicates a performance above planned.
- CPI – Cost Performance Index – this index measures the value of the work completed vs actual cost. A value above 1.0 indicates a cost underrun and a good shape.
- Risk Register – a document which contains information for all registered risks.
- Qualitative Risk Analysis – estimating risk probability and impact using various techniques.
- Quantitative Risk Analysis – using numbers for providing more risk details.
- Risk responses – the process of outlining strategic options, and defining actions, to increase opportunities and reduce threats related to a project.
